Learn About Guitar Tonewood

Learn About Guitar Tonewood
When you're on the hunt for a new acoustic guitar, some understanding of guitar tonewoods can be really useful. These tonewoods—whether spruce, cedar, mahogany or rosewood — play a huge role in shaping the guitar’s sound and personality. For instance, spruce tops are known for their bright, clear sound, while cedar tops are known for a warmer, richer tone. The tonewood you choose greatly affects the guitar's tonal response, resonance, and playability, so knowing which combinations suit your desired tone will help you make a better decision when embarking on your journey of guitar discovery. And don't forget, as solid tonewoods age, they will mature, making your guitar sound better and better, adding depth and complexity and ensuring that your new guitar not only sounds amazing straight away, but also continues to improve as it ages along with you.
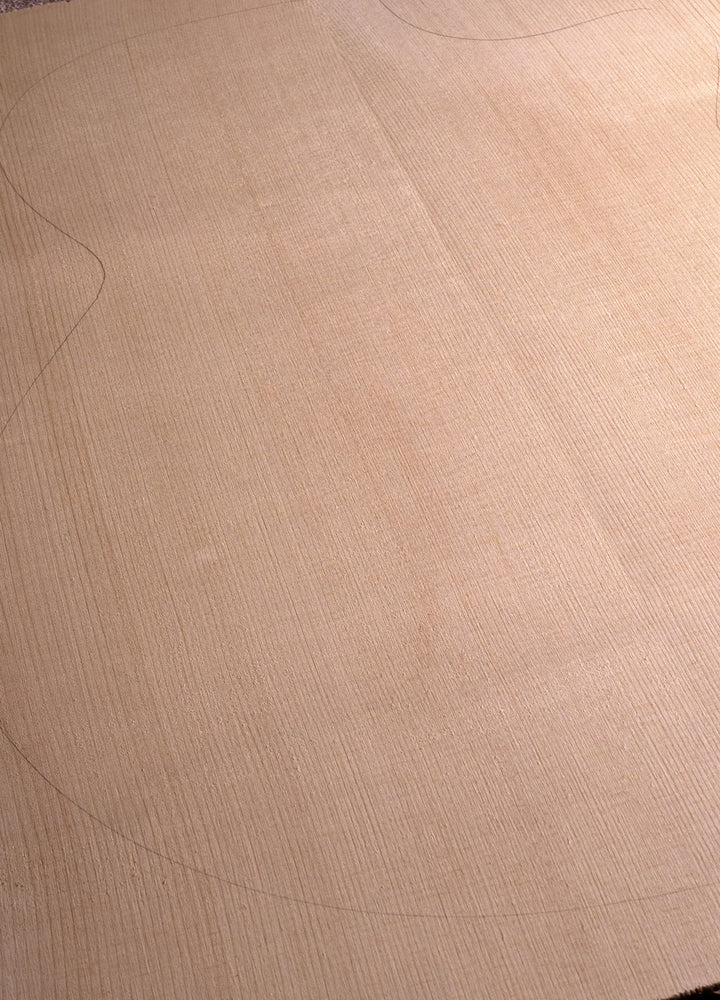

Spruce (Engelmann)
Where Does Engelmann Spruce Come From:
Engelmann Spruce (Picea Engelmannii) finds its native habitat in the elevated territories of the Rocky Mountains and the West Coast of North America. Thriving in these challenging environments, it becomes a prime choice for crafting acoustic guitar soundboards. The cool, high-altitude conditions in which it flourishes contribute to its exceptional tonal characteristics.
Why is Engelmann Spruce Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The selection of Engelmann Spruce for acoustic guitar soundboards is driven by its exceptional tonal attributes. Its relatively low density and high stiffness-to-weight ratio create a winning combination. This allows the wood to vibrate freely, resulting in a balanced and dynamic sound that marries clarity and complexity.
How Does Engelmann Spruce Look:
Engelmann Spruce showcases a palette of colors that range from pale cream to light reddish-brown. Its grain patterns are often subtle and fine, although occasionally with pronounced 'bearclaw' figuration.
How Does Engelmann Spruce Sound:
Engelmann Spruce's tonal profile is characterized by an emphasis on midrange frequencies. This tonal quality makes it particularly suitable for fingerstyle playing and genres that require nuanced note articulation. The wood's sound strikes a balance between warmth and clarity, offering a rich and expressive tonal range. Its responsiveness to touch allows for a wide spectrum of dynamics and tonal variations when used expertly.
As the instrument is played and matures over time, Engelmann Spruce undergoes subtle tonal changes. This natural aging process contributes to the development of a more mature and refined sound. The wood's tonal depth and complexity deepen, adding to the instrument's character and charm.
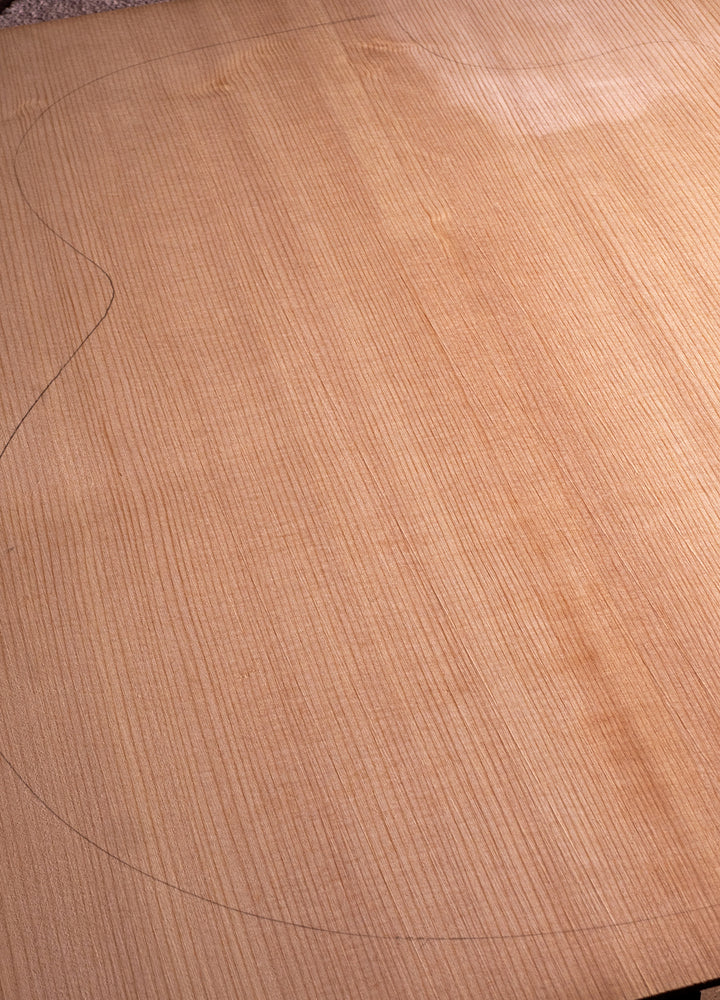

Spruce (Sitka)
Where Does Sitka Spruce Come From:
Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis) finds its natural habitat in the coastal forests of North America's Pacific Northwest, thriving in regions stretching from Alaska to British Columbia, even as far down as California. Known for its strength, light weight, and exceptional tonal clarity, this tonewood has long been a preferred choice for crafting acoustic guitar soundboards.
Why is Sitka Spruce Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The selection of Sitka Spruce for acoustic guitar soundboards is driven by its exceptional tonal attributes. Its moderate density and stiffness-to-weight ratio contribute to a balanced tonality that combines power, projection, and clarity.
How Does Sitka Spruce Look:
Sitka Spruce presents a visual palette ranging from pale cream to light amber. Its grain pattern is often straight and fine, adding to the wood's understated yet inviting aesthetics. This visual charm makes it a favoured choice for luthiers seeking both tonal and visual excellence.
How Does Sitka Spruce Sound:
Sitka Spruce's tonal signature is marked by a balanced combination of power, projection, and clarity. Its well-defined midrange frequencies offer focused presence, making it an ideal choice for both ensemble playing and solo performances. Guitarists will appreciate its responsiveness and the broad range of dynamics it offers. Sitka spruce is also very durable and can withstand a lot of wear and tear: ideal for players with a hectic gigging schedule.
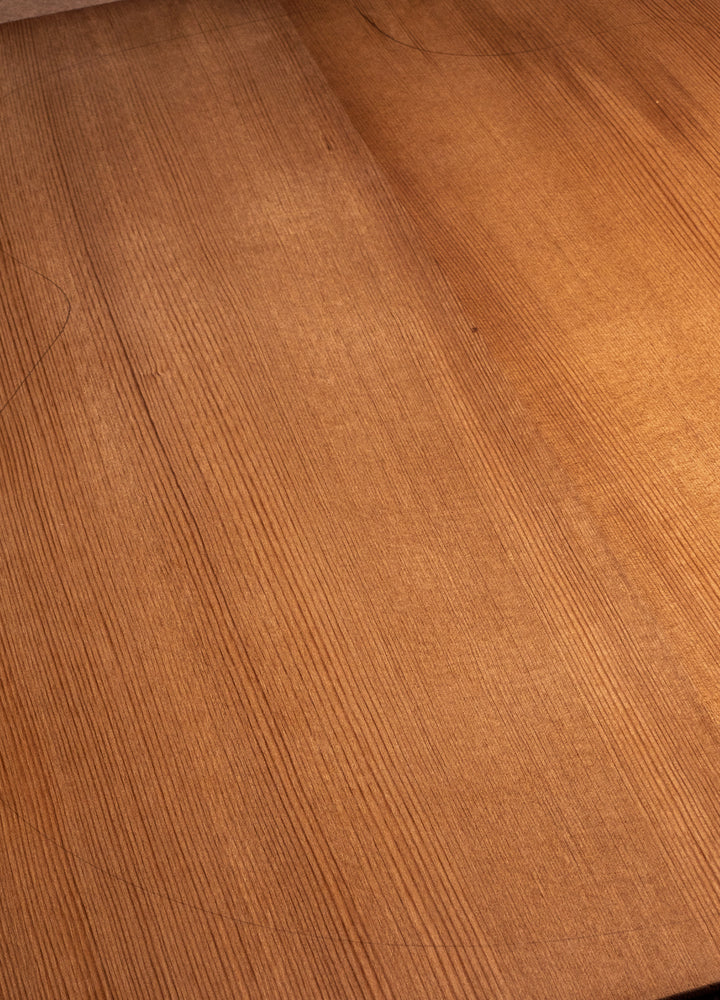

Torrefied Sitka Spruce
Where Does Torrefied Sitka Spruce Come From:
Sitka Spruce, scientifically labeled as Picea sitchensis, originates from the coastal forests of the Pacific Northwest, however, what sets Torrefied Sitka Spruce apart is the specialized thermal treatment it undergoes. This process, known as torrefaction (or torrefication) involves subjecting the wood to carefully controlled heat, altering its cell structure and chemical composition.
Why is Torrefied Sitka Spruce Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The use of torrefied Sitka Spruce for acoustic guitar soundboards stems from its remarkable tonal transformation. Through torrefaction, the wood's physical properties are altered, resulting in improved stiffness, stability, and responsiveness. These modifications contribute to a mature and nuanced tonal quality in the finished guitar.
How Does Torrefied Sitka Spruce Look:
Torrefied Sitka Spruce looks beautiful, adorned with a color spectrum spanning a range of honey, caramel or amber hues. The torrefaction process can also enhance the wood's grain patterns, making them more pronounced and visually appealing. This visual enhancement adds an extra layer of aesthetic charm to the instrument too.
How Does Torrefied Sitka Spruce Sound:
The tonal excellence of torrefied Sitka Spruce is its crowning achievement. The thermal treatment imbues the wood with enhanced warmth, resonance, and complexity. Guitarists will appreciate its ability to project sound with heightened clarity and articulation and the resulting tonal palette allows for a richer, more expressive musical experience, whether strumming chords or playing intricate melodies.
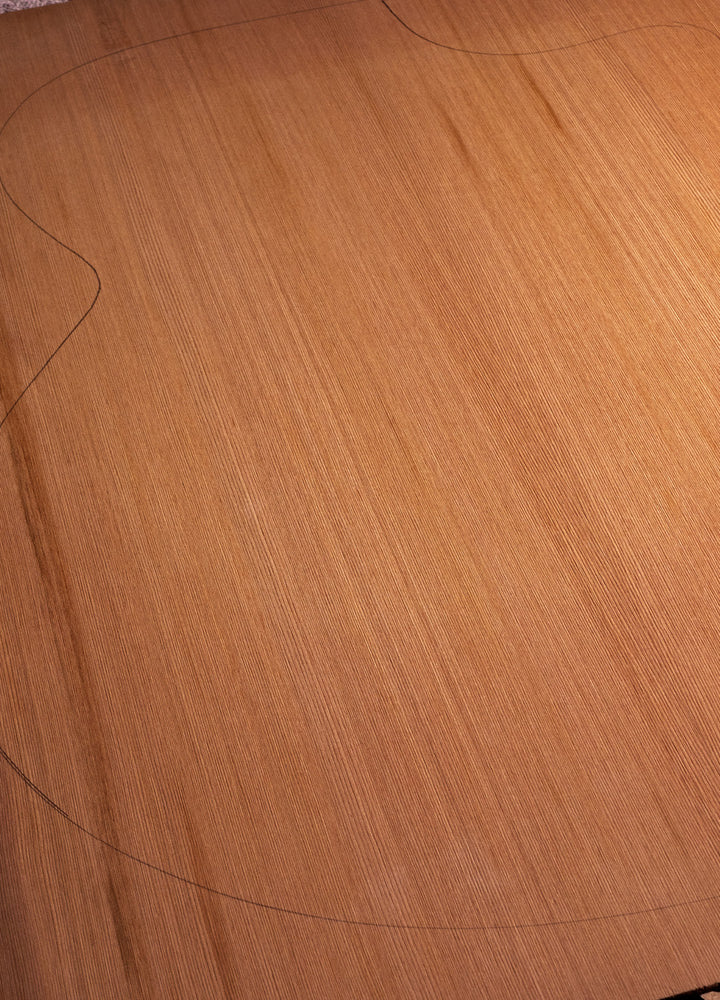

Red Cedar
Where Does Red Cedar Come From:
Red Cedar, scientifically referred to as Thuja plicata, is a cherished tonewood originating from the coastal forests of the Pacific Northwest, although it can also be found in Northern Europe or Australasia. It has distinctive tonal and visual characteristics that make it a sought-after choice among luthiers and musicians.
Why is Red Cedar Used for Acoustic Guitars:
Red Cedar's selection for acoustic guitar soundboards is rooted in its exceptional sonic properties. Its lightweight nature, coupled with its ability to resonate well - although technically quite not as well as Spruce - has long made it a preferred tonewood for crafting the top of guitars, in particular classical guitars. The tonal characteristics are a little more mellow than Spruce owing to its slightly less-stiff structure.
How Does Red Cedar Look:
Red Cedar boasts a visual charm characterized by warm and creamy reddish-brown hues. The wood's grain pattern is usually straight and fine, although a little variance is common, with no negative tonal impact.
How Does Red Cedar Sound:
Red Cedar produces a warm and balanced sound that is characterized by rich overtones and harmonics. The wood's unique tonal properties contribute to a guitar's expressive capabilities, allowing player the ability to transition seamlessly between soft, delicate passages and powerful, resonant chords. Hence its use in classical guitar building for many years.
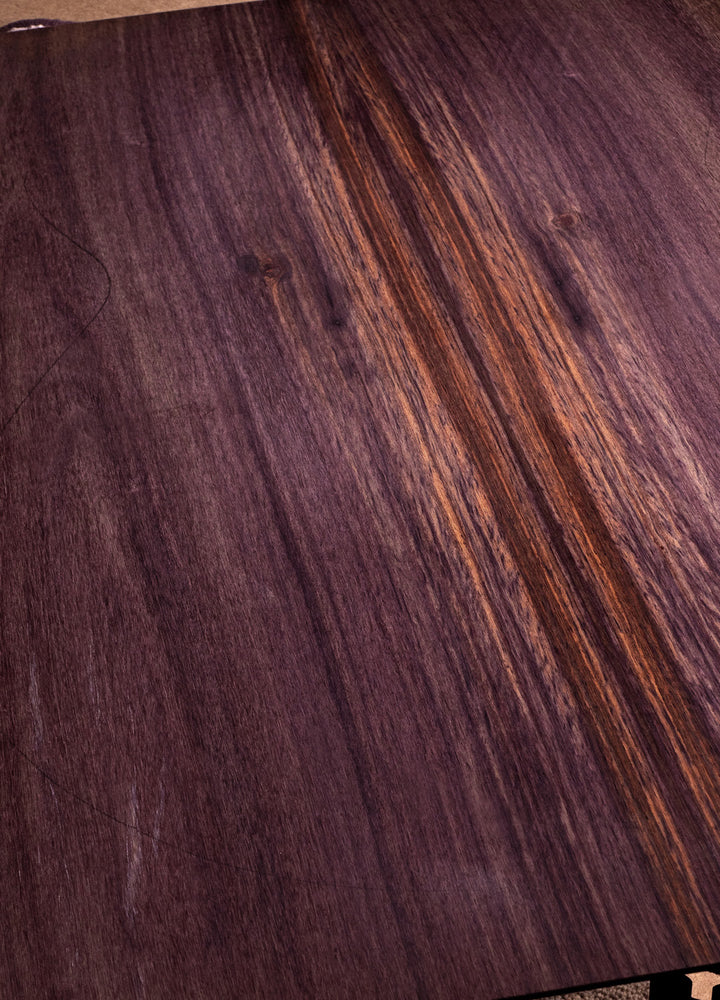

Rosewood (Indonesian)
Where Does Indonesian Rosewood Come From:
Indonesian Rosewood (Dalbergia latifolia) finds its home in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia, with Indonesia serving as a significant source of this prized tonewood, now most commonly as part of managed plantations. The wood's growth in these lush and humid environments contributes to the exceptional tonal attributes that make it an attractive choice for crafting acoustic guitars.
Why is Indonesian Rosewood Used for Acoustic Guitars:
Indonesian Rosewood's reputation as a tonal gem is one of the primary reasons for its use in crafting acoustic guitars. It is often chosen for the back and sides of the guitar due to its rich and resonant tonal properties. The wood's ability to contribute clarity, and a lush harmonic palette to the instrument's voice makes it a favoured choice among luthiers and musicians. Every knows that a guitar with rosewood back and sides will be bright and powerful.
How Does Indonesian Rosewood Look:
Indonesian Rosewood looks beautiful and exudes class and elegance, characterized by deep brown to purple and reddish hues. The wood's grain patterns are intricate with frequent wavy grain patterns and even areas of lighter sapwood for added visual impact. This is in contrast to Indian Rosewood, which tends to be generally straighter and calmer in grain pattern as well as marginally stiffer too.
How Does Indonesian Rosewood Sound:
The tonal characteristics of Indonesian Rosewood contribute to its sonic splendor. The wood will produce a bright yet balanced sound that carries a lush harmonic palette. Rosewood is especially sought after by fingerpickers who need lots of separate note definition, but overall the wood's tonal complexity adds such depth and dimension that it will excel in most any playing style or genre.
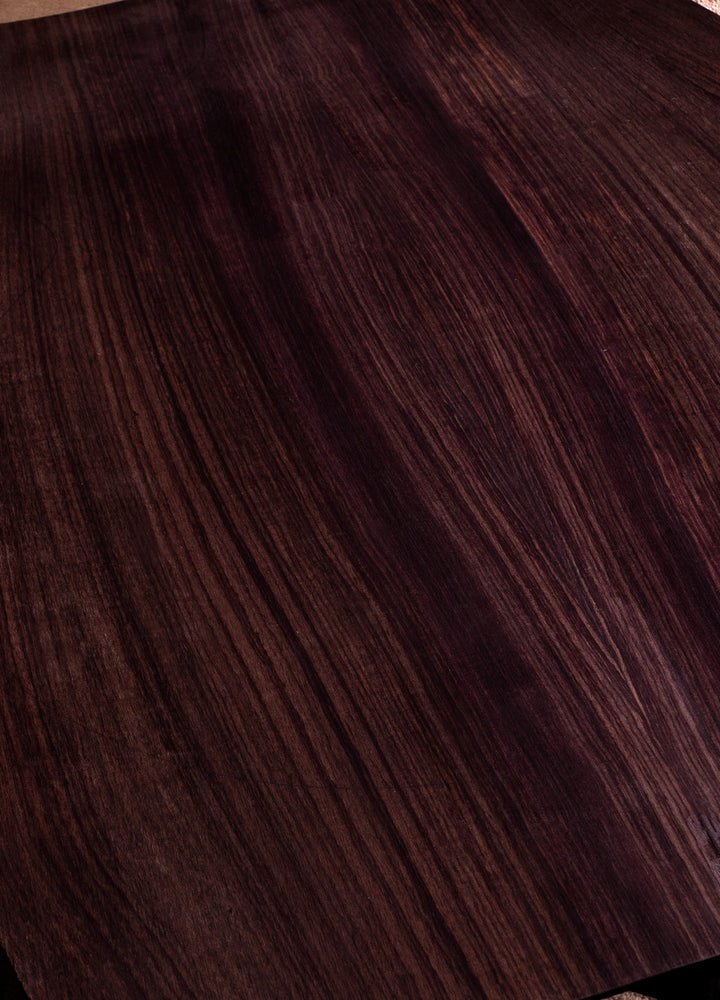

Rosewood (Indian)
Where Does Indian Rosewood Come From:
Indian Rosewood (also Dalbergia Latifolia) finds its natural habitat in the tropical landscapes of the Indian subcontinent. Regions like India and Sri Lanka serve as significant sources of this prized tonewood. The wood's growth in these lush and humid environments contributes to the exceptional tonal attributes that make it an ideal choice for crafting acoustic guitars, and also influences its appearance too.
Why is Indian Rosewood Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The exceptional tonal qualities of Indian Rosewood make it a preferred choice for crafting the back and sides of acoustic guitars. Its tonal characteristics contribute brilliance and a wonderful resonance to the instrument's voice, enhancing its overall tonal profile.
How Indian Rosewood Differs from Indonesian Rosewood:
Indian Rosewood differs from Indonesian Rosewood in several ways. While both woods share some tonal qualities, Indian Rosewood is generally considered to have a slightly warmer and richer tonal character; it has potential to produce more tonal sustain and overtone content; and it tends to look more visually uniform than Indonesian Rosewood.
How Does Indian Rosewood Look:
Indian Rosewood is generally straighter in grain and less varied in colouration when compared to Indonesian Rosewood. Its color spectrum will still span from deep browns to purples, but with less frequency and with less of a showy nature.
How Does Indian Rosewood Sound:
The tonal characteristics of Indian Rosewood contribute to its sonic brilliance. Being a little stiffer than Indonesian Rosewood, Indian Rosewood produces a balanced sound that is characterized an unbeatable level of articulation and harmonic response.
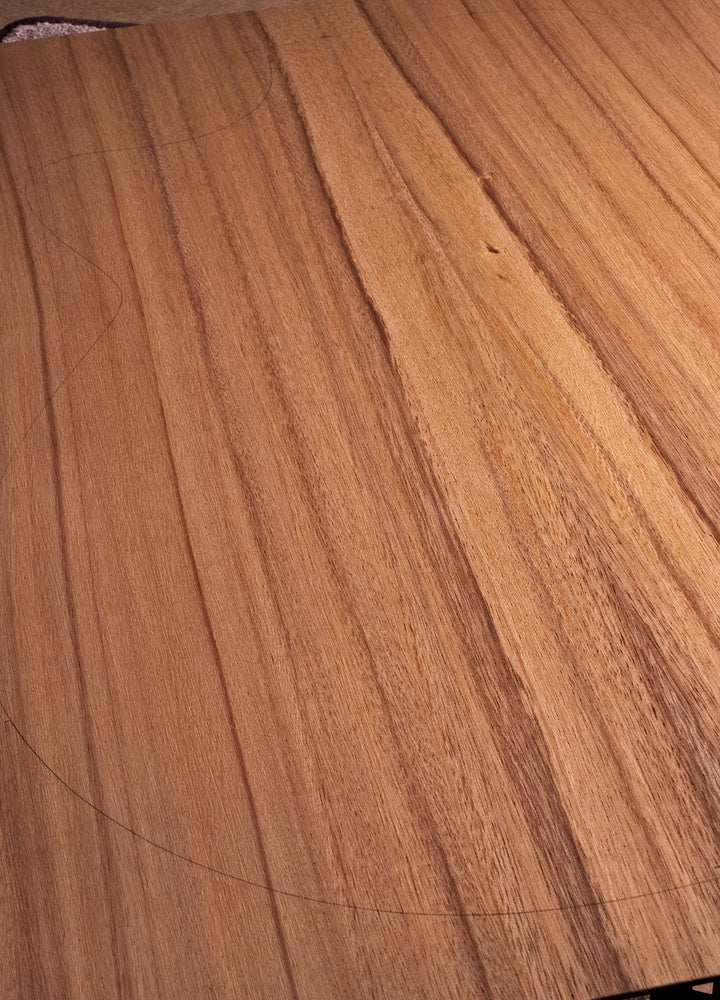

Java Trembesi
Where Does Trembesi Come From:
Trembesi wood, scientifically labeled as Samanea Saman, finds its natural habitat in the tropical regions of Southeast Asia, with Indonesia being a notable source where the trees grow freely. The wood's growth patterns in these lush and humid environments contributes to the unique tonal attributes that make it an appealing choice for crafting acoustic guitar soundboards.
Why is Trembesi Used for Acoustic Guitars:
Both the unique visual and tonal characteristics of Trembesi wood make it a great choice for making acoustic guitars. Its tonal profile contributes warmth and a balanced sonic spectrum, especially suited to chordal tones and accompaniment, plus - as you may have already noticed - it is visually beautiful with an endless array of variation.
How Does Trembesi Look:
Trembesi wood showcases a captivating visual appeal, with a range of colors that span from light creams to dark browns, often accompanied by intricate and visually pleasing grain patterns: sometimes near vertical and sometimes flamed or almost quilted. Faith Guitars' luthiers love the diverse possibilities that Trembesi wood offers, allowing them to create instruments that are not only sonically exceptional but also visually striking.
How Does Trembesi Sound:
Trembesi produces a warm and balanced sound enriched with good harmonic response too. This lovely tonewood offers a truly nuanced sonic palette.
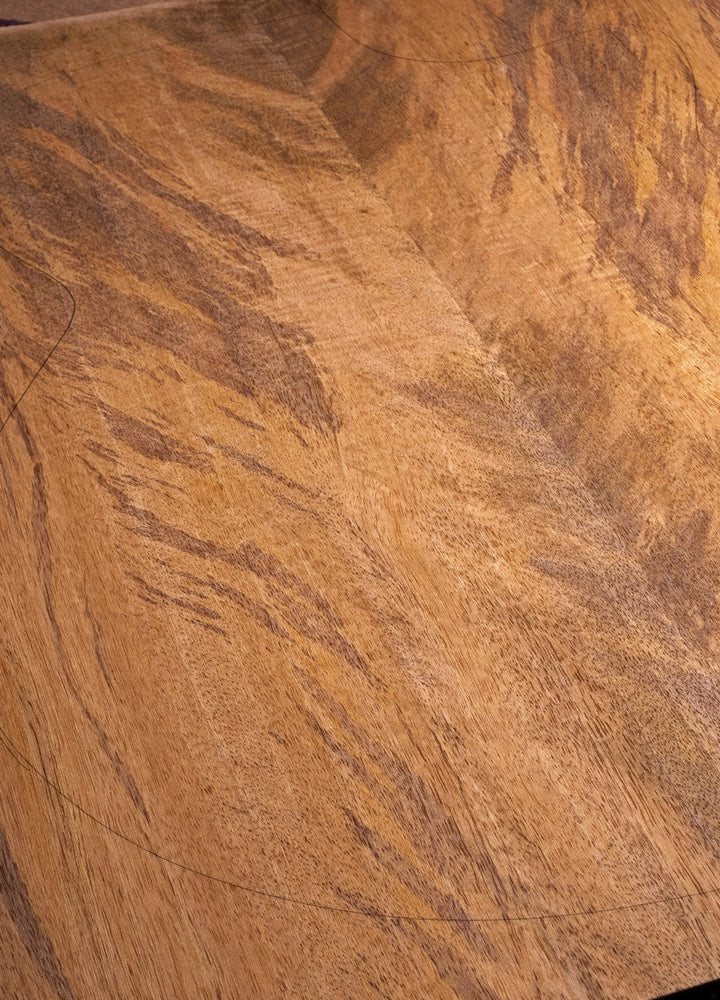

Java Mango
Where Does Mango Wood Come From:
Indonesian Mango Wood (Mangifera indica) finds its natural habitat in the tropical regions of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia. Mango trees grow abundantly across Indonesia, both in the wild and in managed fruit plantations, but wherever possible we seek out the wood from fruit plantation management. Indonesia's warm and humid environments contributes to the unique tonal and visual attributes that make it an extremely appealing choice for crafting acoustic guitars.
Why is Mango Wood Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The use of Indonesian Mango Wood for acoustic guitars goes beyond tonal considerations, although the fascinating sound profile is certainly worthy of note. In fact, using mango is a sustainable practise as the trees are felled as part of the mango orchards management process, and replacement trees are relatively fast growing too.
How Does Mango Wood Look:
Indonesian Mango Wood presents an alluring visual charm, characterized by a range of natural colours from golden to reddish-brown. The wood often has distinctive figure patterns, such as curly, flamed or quilted grain, adding a touch of uniqueness, especially when carefully stained.
How Does Mango Wood Sound:
Indonesian Mango produces a balanced and warm, with a little less treble than mahogany or trembesi. The wood's tonal spectrum features a pleasing midrange emphasis, which enhances the guitar's sound projection and adds depth to the overall sonic character. As we have noted in relation to the popular Blue Moon series of Faith Guitars, Mango is the most noticeably different-sounding tonewood we have ever used.
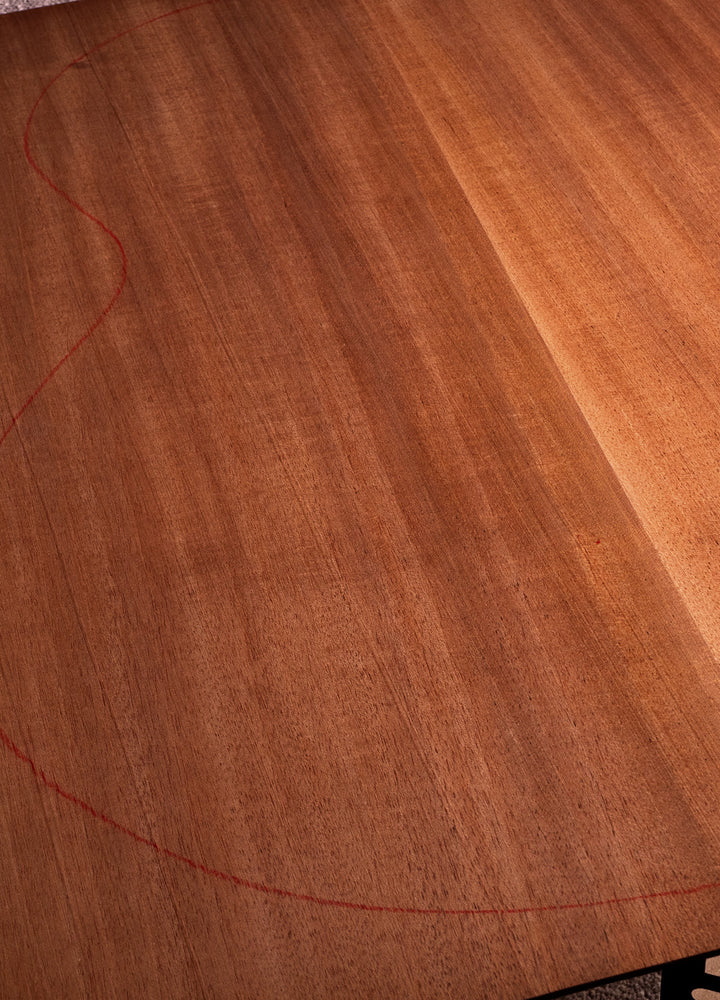

Mahogany (Indonesian)
Where Does Indonesian Mahogany Come From:
Indonesian Mahogany (Swietenia mahagoni) finds its natural habitat in the lush tropical regions of Southeast Asia, growing commonly in Indonesia, as the wood thrives in environments with well-drained soils and warm, humid climates. These ideal conditions contribute to the wood's exceptional growth - often around 30m in height - and its unique tonal attributes.
Why is Indonesian Mahogany Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The use of Indonesian Mahogany for acoustic guitars is rooted in its tonal excellence. Mahogany in all its varieties has long been a favourite amongst guitar builders, as it imparts a warm tonal character without sacrificing too much high-end. The wood's resonant properties contribute to a well-rounded sound that is suitable for a variety of playing styles and musical genres.
How Does Indonesian Mahogany Look:
Indonesian Mahogany boasts a distinctive appearance, characterized by its orange-to-brown colouration, sometimes with darker streaks and subtle flaming, creating a sense of dimension. The comparative simplicity of its appearance makes the staining or colouration process reliable and effective, leading to many possibilities.
How Does Indonesian Mahogany Sound:
Indonesian Mahogany produces a warm and inviting sound with a notable midrange prominence. The wood offers notable natural sustain too, adding additional depth and character to the guitar's voice. When paired with a Spruce top, the sound is bright yet still warm, when paired with Mahogany on the top too, the sound becomes noticeably darker without as much 'zing', but with a deeper overall character.
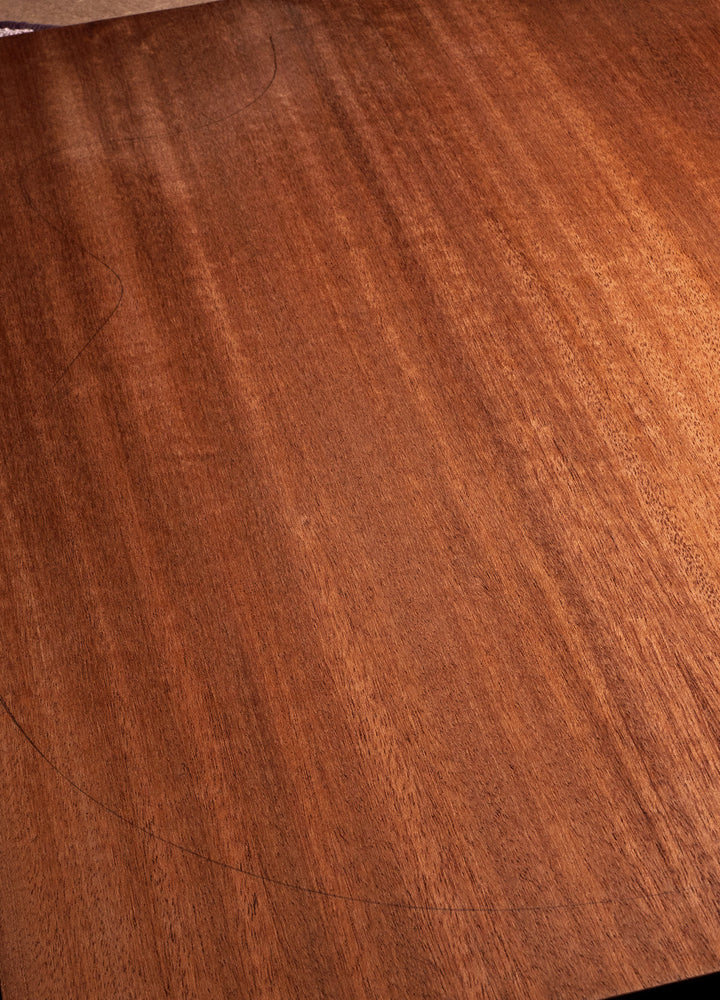

Mahogany (African Khaya)
Where Does Khaya Mahogany Come From:
African Khaya Mahogany (Khaya Ivorensis) finds its natural habitat in the tropical rainforests of West and Central Africa in countries such as Cameroon, Ghana, and Nigeria. Timber for guitar-making is generally sourced from specialist European tonewood merchants in relatively small quantities.
Why is Khaya Mahogany Used for Acoustic Guitars:
The use of African Khaya Mahogany for acoustic guitars is driven by its exceptional tonal properties. It offers tonal clarity, balanced resonance, and responsiveness, making it an ideal choice for guitar tops, backs, and sides. The wood's ability to enhance the instrument's tonal palette contributes to a versatile and expressive sound.
How Does Khaya Mahogany Look:
Khaya Mahogany showcases an aesthetic elegance characterized by reddish-brown hues, somewhat darker in colour than the often orange of Indonesian Mahogany. Its interlocking grain patterns are subtly beautiful and elegant.
How Does Khaya Mahogany Sound:
African Khaya Mahogany is a little stiffer than Indonesian Mahogany and therefore helps produce a brighter tone. When matched with Spruce, the resulting sound is closer to rosewood's 'brilliance', and when used for Top, Back and Sides, the sound is deep and mellow with remarkable articulation.
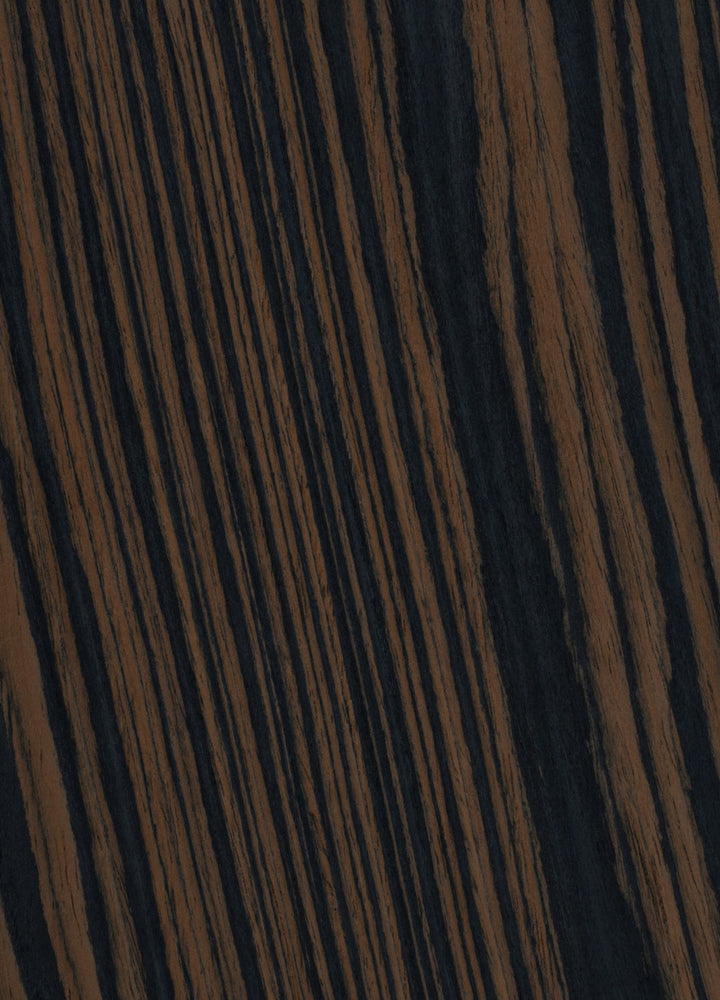
Indonesian (Macassan) Ebony
Where Does Indonesian Ebony Come From:
Indonesian Ebony (Diospyros celebica) finds its natural habitat in the lush tropical regions of Southeast Asia, in particular Macassar, Indonesia. This region gives rise to the stunning striped character that can be found on Faith Guitars' fingerboards and fittings.
Why is Indonesian Ebony Used for Acoustic Guitar Fittings:
The use of Indonesian Ebony for acoustic guitar fingerboards and bridges is driven by its exceptionally hardwearing properties. Its strength and stability make it ideal for enduring the tension, stress and wear exerted by guitar strings.
How Does Indonesian Ebony Look:
In contrast to the more common Indian Ebony, Indonesian Ebony has a striking appearance characterized by a deep black colour with visible stripes and streaks. These streaks or variations in color add visual interest and uniqueness to the guitar's fingerboard, bridge, and bridge pins. You can also find Indonesian Ebony on the tuning pegs of many higher-end Faith guitars, although we do stain these to make them more uniformly black.
Why is Hardwood Important for Guitar Fingerboards and Bridges:
The choice of a quality hardwood, such as Indonesian Ebony, for guitar fingerboards and bridges is crucial not only because of its strength and durability, but hardwoods - like Indonesian Ebony - also contribute to the transfer of vibrations, which is essential for producing clear and resonant tones. This is why identical instruments with differing fingerboard materials can sound markedly different.